Welcome! Schedule A Radon Test Today
Important Facts About Radon
What Is Radon?
Radon is an invisible radioactive gas that is odorless, colorless, and tasteless. In form in the soil beneath our homes. Radon is a radioactive gas that forms naturally when uranium, thorium or radium, which are radioactive metals break down in rocks, soil and groundwater. As part of the radioactive decay process, radon gas is produced. The gas moves up through the soil to the surface. This is mixed within the air and enters homes, schools and workplaces through cracks and openings through the foundation. In some cases radon can enter buildings through well water and come from building materials. Radon is referred to as the "silent killer". It is the 2nd leading cause of lung cancer. 1 in 15 homes have high levels of radon.
All Homes/Buildings Have Radon.
Any home can have a radon problem and everyone home and building has some sort of radon level. Old or new homes, well sealed homes and drafty homes. Homes with basements and without. Radon concentration is higher indoors than outdoors. Radon has been around for along time however its became a problem in the last 20 years or so since the energy crisis has let to a "tighter" construction of more energy efficient homes. Years ago when the energy was cheaper, homes were made draftier and had built-in air leaks which helped dilute indoor contaminants like radon to a safe level. However as energy costs rose, home construction became higher resulting in risen indoor radon levels.
Top 10 States With the Highest Levels.
- Alaska (10.7)
- South Dakota (9.6)
- Pennsylvania (8.6)
- Ohio (7.8)
- Washington (7.5)
- Montana (7.4)
- Kentucky (7.4)
- Idaho (7.3)
- Colorado (6.8)
- West Virginia (6.1)

How Radon Enters a House.
Radon gas comes from the soil. Even houses with new foundations can have high radon levels. The gas can enter the foundation through cracks in the floor and walls, floor drains and sump openings, and holes made for pipes and utility lines. Radon gas that comes from the basement or crawl space will then migrate upstairs into the main living areas. Radon can also be present in well water. Radon gas can enter the house as people take showers and baths or running water for other uses. However this source of radon is not usually as significant as the soil.

How Radon Is Measured.
Radon is measured in PicoCuries per Liter.
For perspective the national average of outdoor and indoor air:
- Outdoor air level is 0.4pCi/L
- Indoor air level is 1.3pCi/L
The maximum "acceptable" level of radon in a home is 4.0pCi/L
If your levels are 4.0 or above the EPA recommends fixing your home by contacting a professional radon mitigator

Types of Devices Used to Test Radon.
~Passive
- Require no power
- Alpha track detectors
- Charcoal Canisters
- Charcoal liquid scintillation dectectors
These can be found in certain stores or online. They take 2 days to test and then they must be turned into laboratory for analysis.

~Active
- Require power
- Continuous monitors
- Continuous working level monitors
These tests provide data on the range of variation within a given test period.They are 99% certainty. The monitor sits on a tripod stand.
Common Factors That Influence Results.
Time of Year- Radon levels are highest during the winter months.
The Location of The Test- EPA recommends testing for radon in the lowest livable level of your home. This is where radon levels are usually the highest.
Weather Patterns- Stormy weather and high winds effects the radon measurement.
Testing Interference- The monitor cannot be touched, moved or tampered with. Exterior doors and windows must be kept closed 12 hours prior and during the test (except for normal entry and exit).

Is It Okay to Live With Radon?
Radon is a health hazard with simple solutions. Removing radon is relatively simple. Having your home tested by our certified Ohio radon inspectors from Radon Investigators in Cleveland/Northeast Ohio area is an effective way to determine whether you and your family are at risk of high radon exposure. Some other factors include:
- The location where you spend most of your time.
- The amount of time spend in your home.
- Whether you are a smoker or have ever smoked.
- Whether you burn wood, coal, or other substances that adds particles to the indoor air.

What Does Radon Do to Your Health?
Radon gas in the air breaks down into tiny radioactive elements (radon progeny). When you breathe in radon, the elements get into the lining of your lungs and gives off radiation. Over time that can damage the cells there and lead to lung cancer. Radon is responsible for about 21,000 lung cancer deaths each years in the United States. It usually takes 5 to 25 years to develop.
Possible symptoms include; shortness of breath, difficult breathing, new or worsening cough, pain or rightness in the chest, hoarseness or trouble swallowing.
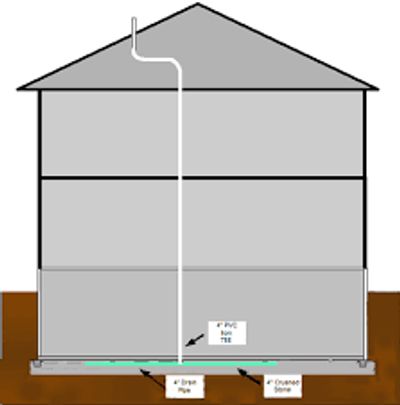
How to Get Rid of Radon.
You cannot get rid of radon. Every building has some sort of level of radon in the soil beneath it. However you can reduce the levels by a process called radon mitigation.
There are 2 different types of Radon Mitigation Systems.
Passive Radon Mitigation System.
A passive radon mitigation system is typically installed when a home is being constructed. A passive contains two components:
- A PVC ventilation pipe that extends from beneath the slab up to the eave line of the roof.
- a physical barrier between the soil and house foundation.
Passive system relies on natural pressure differentials and air currents to eliminate radon from the home.
Sometimes when a home is being built, the building company will install a passive system without ever testing the home for radon
This can be a problem because passive radon systems do not bring extremely high levels of radon below the EPA recommended 4.0. Many home buyers do not realize this when purchasing a home with a passive system.

Active Mitigation System.
An active radon mitigation system is installed when the home contains elevated levels of radon. It called active because a fan is always pulling radon from beneath the home therefore it doesn't have the opportunity to enter. This is also called sub-slab depressurization method.
Active system has 4 components:
- Electric vent fan.
- System failure warning device called u-tube manometer.
- Ventilation pipe running from the sub-slab of the basement up above the eave line of the roof or in the garage attic.
- Sealed and Caulked cracks in the foundation.
Theres several ways an Active system can be installed depending on the layout of the home. The average radon mitigation system can be installed for under $1500.
Contact Us Now
Copyright © 2021 Radon Investigators - All Rights Reserved.
Powered by GoDaddy
This website uses cookies.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.